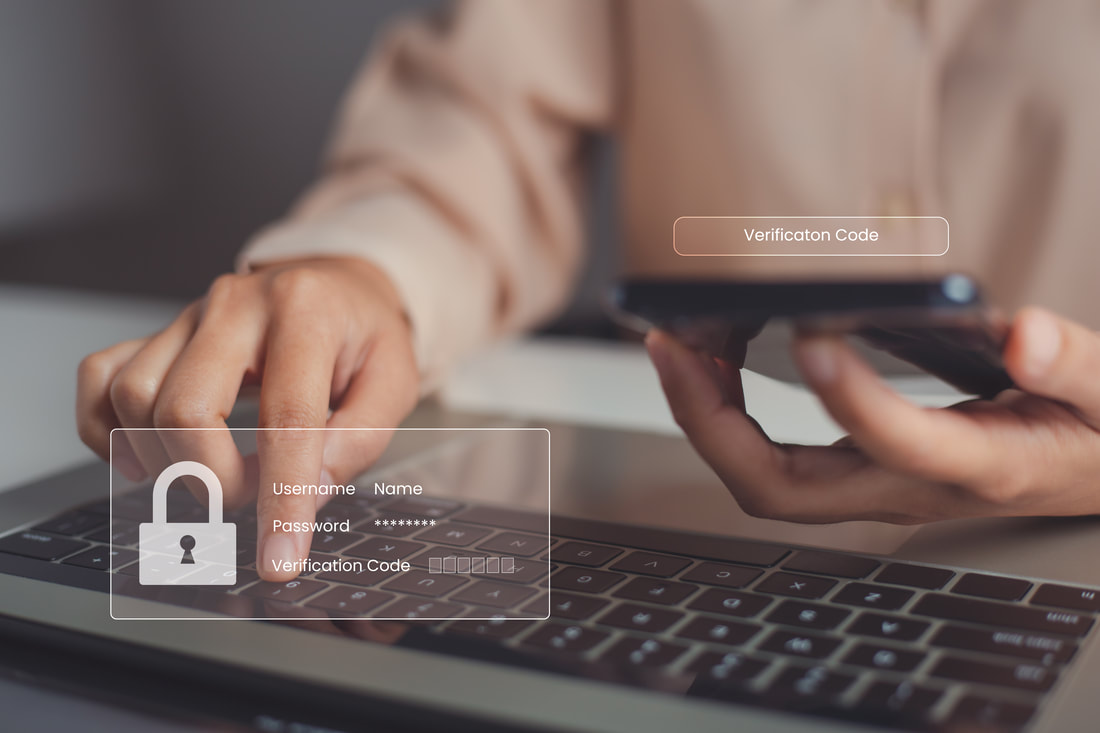
In today's digital age, weak passwords have become a significant vulnerability, leaving individuals and organisations at risk of cyberattacks and data breaches. Alongside this, the rising prominence of two-factor authentication (2FA) has proven to be an essential defence in safeguarding our digital identities and sensitive information.
The Danger of Weak Passwords:
Weak passwords are the Achilles' heel of cybersecurity. These passwords lack complexity and are easily guessable, making them susceptible to brute-force attacks and password-cracking tools. Common weak passwords include "password123," "qwerty," and "123456," which are embarrassingly easy for cybercriminals to exploit.
Compromised passwords open the door for unauthorised access to personal accounts, social media profiles, email addresses, financial information, and even corporate networks. The consequences of such breaches can be devastating, leading to identity theft, financial loss, reputational damage, and more.
The Importance of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a powerful additional layer of security that addresses the shortcomings of weak passwords. It requires users to provide two distinct forms of identification before gaining access to an account or system. Typically, 2FA consists of the following factors:
1. Something you know: This is usually the traditional password or PIN.
2. Something you have: A second factor, often a unique code generated by a smartphone app, a text message sent to your phone, or a physical token.
The implementation of 2FA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorised access, even if someone manages to obtain your password. This is because the second factor adds an extra hurdle for attackers, making it much harder to breach your account.
Benefits of 2FA:
1. Enhanced Security: 2FA acts as a robust barrier against password-related attacks, significantly reducing the likelihood of unauthorised access.
2. Protection from Credential Stuffing: Cybercriminals often use username and password combinations from previous breaches to attempt access across multiple platforms. 2FA prevents such automated attacks as the additional factor must be provided.
3. Peace of Mind: Users can rest assured that even if their password is compromised, their account remains secure due to the added layer of authentication.
4. Industry Compliance: Many regulatory standards and frameworks require organisations to implement 2FA for secure access to sensitive data and systems.
5. User-Friendly Implementation: With the advancement of technology, 2FA has become more convenient, such as biometric authentication (fingerprint, facial recognition), reducing friction for users while maintaining high security.
In conclusion, weak passwords leave us vulnerable to cyber threats and potential data breaches, but we can take proactive steps to protect ourselves. Embracing two-factor authentication adds an invaluable layer of security to our digital lives, making it significantly harder for attackers to compromise our accounts. By adopting 2FA and practicing strong password hygiene, we can fortify our defences against cyber adversaries and enjoy a safer online experience.
The Danger of Weak Passwords:
Weak passwords are the Achilles' heel of cybersecurity. These passwords lack complexity and are easily guessable, making them susceptible to brute-force attacks and password-cracking tools. Common weak passwords include "password123," "qwerty," and "123456," which are embarrassingly easy for cybercriminals to exploit.
Compromised passwords open the door for unauthorised access to personal accounts, social media profiles, email addresses, financial information, and even corporate networks. The consequences of such breaches can be devastating, leading to identity theft, financial loss, reputational damage, and more.
The Importance of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a powerful additional layer of security that addresses the shortcomings of weak passwords. It requires users to provide two distinct forms of identification before gaining access to an account or system. Typically, 2FA consists of the following factors:
1. Something you know: This is usually the traditional password or PIN.
2. Something you have: A second factor, often a unique code generated by a smartphone app, a text message sent to your phone, or a physical token.
The implementation of 2FA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorised access, even if someone manages to obtain your password. This is because the second factor adds an extra hurdle for attackers, making it much harder to breach your account.
Benefits of 2FA:
1. Enhanced Security: 2FA acts as a robust barrier against password-related attacks, significantly reducing the likelihood of unauthorised access.
2. Protection from Credential Stuffing: Cybercriminals often use username and password combinations from previous breaches to attempt access across multiple platforms. 2FA prevents such automated attacks as the additional factor must be provided.
3. Peace of Mind: Users can rest assured that even if their password is compromised, their account remains secure due to the added layer of authentication.
4. Industry Compliance: Many regulatory standards and frameworks require organisations to implement 2FA for secure access to sensitive data and systems.
5. User-Friendly Implementation: With the advancement of technology, 2FA has become more convenient, such as biometric authentication (fingerprint, facial recognition), reducing friction for users while maintaining high security.
In conclusion, weak passwords leave us vulnerable to cyber threats and potential data breaches, but we can take proactive steps to protect ourselves. Embracing two-factor authentication adds an invaluable layer of security to our digital lives, making it significantly harder for attackers to compromise our accounts. By adopting 2FA and practicing strong password hygiene, we can fortify our defences against cyber adversaries and enjoy a safer online experience.


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed